Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wakui, Takashi; Yamasaki, Kazuhiko*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Jikken Rikigaku, 22(2), p.96 - 104, 2022/06
Pulsed laser irradiation and indentation tests on radiation shielding glasses and a lead-free glass were carried out. The size of irradiation damage of the glass with high lead content was larger than that with low content. The micro plastic behavior of glasses was quantitatively determined using the inverse analyses based on indentation results. Flow stress decreased with an increase of lead content and that in irradiated area was lower than that in unirradiated area. On the other hand, plastic flow resistance increased with an increase of the lead content and that in irradiated area was higher than that in unirradiated area. Fracture energy and critical size of plastic zone around tip of crack in unirradiated and irradiated areas were calculated based on experimental results including constants evaluated using the inverse analysis. These values decreased with an increase of the lead content and these values in irradiated area were lower than that in unirradiated area.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yomogida, Takumi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 123(1), p.817 - 824, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:53.94(Chemistry, Physical)Reaction kinetics of laser-induced particle formation in an aqueous solution of PdCl
 was investigated by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS). The Pd particle was generated by irradiation of nanosecond pulsed 266-nm laser. The TEM observation showed dependence of the particle size on the laser fluence and promotion of the particle growth by irradiation of high-fluence laser. The DXAFS data give us the Pd
was investigated by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS). The Pd particle was generated by irradiation of nanosecond pulsed 266-nm laser. The TEM observation showed dependence of the particle size on the laser fluence and promotion of the particle growth by irradiation of high-fluence laser. The DXAFS data give us the Pd concentration. Temporal changes of the Pd
concentration. Temporal changes of the Pd concentration analyzed based on Finke-Watzky two step mechanism. The analysis elucidates that the laser photon contributes to the reduction of the PdCl
concentration analyzed based on Finke-Watzky two step mechanism. The analysis elucidates that the laser photon contributes to the reduction of the PdCl
 ion by the one-photon process and to the autocatalytic growth of the Pd particles by the multi-photon process.
ion by the one-photon process and to the autocatalytic growth of the Pd particles by the multi-photon process.
 Pd by ICP-MS; The Relation between separation conditions and Pd recovery
Pd by ICP-MS; The Relation between separation conditions and Pd recoveryYomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho; Saeki, Morihisa*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Esaka, Fumitaka; Oba, Hironori*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 66(9), p.647 - 652, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.93(Chemistry, Analytical)Palladium-107 is a long-lived fission product, which can be found in high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW). Determination of the  Pd contents in HLLW is essential to evaluate the long-term safety of HLLW repositories. However, the
Pd contents in HLLW is essential to evaluate the long-term safety of HLLW repositories. However, the  Pd content in HLLW has not been reported because of difficulties in pretreatment for the measurement. In this study, we investigated applicability of laser-induced photoreduction to HLLW solution: it enables a simple and non-contact separation of Pd. The results showed the recovery of 60% was achieved at the conditions: 40% ethanol, 20 min irradiation, 100 mJ of pulse energy. Additionally, major radionuclides and potentially interfering components in ICP-MS were removed from the simulated HLLW over a wide concentration range of Pd from 0.24 to 24 mg L
Pd content in HLLW has not been reported because of difficulties in pretreatment for the measurement. In this study, we investigated applicability of laser-induced photoreduction to HLLW solution: it enables a simple and non-contact separation of Pd. The results showed the recovery of 60% was achieved at the conditions: 40% ethanol, 20 min irradiation, 100 mJ of pulse energy. Additionally, major radionuclides and potentially interfering components in ICP-MS were removed from the simulated HLLW over a wide concentration range of Pd from 0.24 to 24 mg L , showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Oba, Hironori*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Yomogida, Takumi
Denki Gakkai Kenkyukai Shiryo, Denshi Zairyo Kenkyukai (EFM-17-010 021), p.15 - 18, 2017/09
021), p.15 - 18, 2017/09
Irradiation of nanosecond pulsed UV laser into a solution of palladium ion leads to formation of palladium particles with sub-micron size particles by time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao
Isotope News, (739), p.15 - 20, 2015/11
We introduce the multi-charged heavy-ion acceleration mechanisms and the recent results obtained at the KPSI JAEA. We also propose the novel application of the laser-driven multi-charged heavy ion beam.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 57(10), p.677 - 681, 2015/10
, 57(10), p.677 - 681, 2015/10
Light, such as, High intensity short pulse laser interacting with the thin-foil target, accelerates the almost fully stripped Iron ions towards the energy of 0.9 GeV. It is quite difficult for the conventional ion sources to make the highly charged heavy ions within few tens of femtoseconds and at the same time accelerates them towards higher energies. The achievement explained here is one new step towards the novel type compact ion sources.
Abe, Hiroshi; Shimomura, Takuya; Tokuhira, Shinnosuke*; Shimada, Yukihiro*; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Yuta*; Nishimura, Akihiko; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 7th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing (LAMP 2015) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2015/08
A short pulse laser (the nanosecond and femtosecond) was applied to hydrogen absorbing alloys surface layer, and a surface modification experiment was put into effective to aim at improvement of hydrogen adsorption functionally. It was investigated about correlation between an initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate of hydrogen alloys and a laser irradiation in this research. The laser irradiation condition was done with pulse width 100 fsec and energy 0.2 - 3.4 mJ/pulse. It blazed down on hydrogen absorbing alloys (LaNi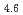 Al
Al ) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Choi, I. W.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Tatsufumi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Daito, Izuru*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(2), p.025001_1 - 025001_9, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.75(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Projection images of a metal mesh produced by directional MeV electron beam together with directional proton beam, emitted simultaneously from a thin foil target irradiated by an ultrashort intense laser. The mesh patterns are projected to each detector by the electron beam and the proton beam originated from tiny virtual sources of  20 micron meter and
20 micron meter and  10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
Nishimura, Akihiko; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Takehiro*; Shimomura, Takuya; Terada, Takaya; Daido, Hiroyuki
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 9(3), p.221 - 224, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heat resistant FBG sensors were developed by femtosecond laser processing to apply them to high temperature operated piping system of nuclear power plants. The FBG sensor was installed on the surface of a steel blade and a vibration test was conducted to detect the resonant vibration frequency of the vibrating blade. The FBG sensor had the heatproof performance at 600 C. A frequency stabilized sensing system using a tunable laser was tested for structural health monitoring in daily operation of nuclear power plants. The FBG sensor was installed on the surface of a steel blade for vibration induced strain measurements. Welding, brazing, soldering and noble metal powder adhesive were discussed for molding the FBG sensors.
C. A frequency stabilized sensing system using a tunable laser was tested for structural health monitoring in daily operation of nuclear power plants. The FBG sensor was installed on the surface of a steel blade for vibration induced strain measurements. Welding, brazing, soldering and noble metal powder adhesive were discussed for molding the FBG sensors.
Nishimura, Akihiko; Terada, Takaya; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Takehiro*; Shimomura, Takuya
Proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-22) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/07
Since 2007, JAEA has been developing laser based technologies of structural health monitoring. The FBG sensor made by femtosecond laser processing will be the best candidate. To make the best use of the heat resistant characteristic, the FBG sensor was embedded in metal mold by laser cladding. A groove was processed to the surface of a SUS metal plate. We used a QCW laser to weld a filler wire on the plate. A series of weld beads perfectly formed a sealing clad on the groove. Though the FBG sensor was buried tightly, no degradation on the reflection spectrum was detected after the processing. The FBG sensor could detect the vibration of the plate caused by impact shocks and audio vibration. The reflection peak of the FBG sensor under laser cladding condition was shifted to be 6 nm. We demonstrated that the corresponded temperature derive from the reflection peak shift reached 600 degrees in heat shock experiments. The installation procedure of a FBG sensor using a portable laser cladding machine was described.
Sherrill, M. E.*; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Dodd, E. S.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
Physical Review E, 73(6), p.066404_1 - 066404_6, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:75.69(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A model that solves simultaneously both the electron and atomic kinetics was used to generate synthetic He X-ray spectra to characterize a high intensity ultrashort laser driven Ar cluster target experiment. In particular, level populations were obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collisional rates were computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero dimensional Boltzmann equation. In addition, aparticle-in-cell simulation was used to model the laser interaction with the cluster target and provided the initial electron energy distribution function (EEDF) for the Boltzmann solver. This study suggests that the high density plasma contribution to the time-integrated He
X-ray spectra to characterize a high intensity ultrashort laser driven Ar cluster target experiment. In particular, level populations were obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collisional rates were computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero dimensional Boltzmann equation. In addition, aparticle-in-cell simulation was used to model the laser interaction with the cluster target and provided the initial electron energy distribution function (EEDF) for the Boltzmann solver. This study suggests that the high density plasma contribution to the time-integrated He spectrum was in a highly non-equilibrium state in both the EEDF and the ion level populations and provides a prediction of 5.7 ps for the average cluster integrity time for this high density state.
spectrum was in a highly non-equilibrium state in both the EEDF and the ion level populations and provides a prediction of 5.7 ps for the average cluster integrity time for this high density state.
Sherrill, M. E.*; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Csanak, G.*; Kilcrease, D. P.*; Dodd, E. S.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Akahane, Yutaka; Aoyama, Makoto; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; et al.
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 99(1-3), p.584 - 594, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:18.42(Optics)In this work, we present a model that solves self-consistently the electron and atomic kinetics to characterize highly non-equilibrium plasmas, in particular for those systems where both the electron distribution function is far from Maxwellian and the evolution of the ion level populations are dominated by time dependent atomic kinetics. In this model, level populations are obtained from a detailed collisional-radiative model where collision rates are computed from a time varying electron distribution function obtained from the solution of the zero-dimensional Boltzmann equation. The Boltzmann collision term includes the effects of electron-electron collisions, electron collisional ionization, excitation and de-excitation. An application for He spectra from a short pulse laser irradiated argon cluster target will be shown to illustrate the results of our model.
spectra from a short pulse laser irradiated argon cluster target will be shown to illustrate the results of our model.
 films by RBS/C
films by RBS/CYamamoto, Shunya; Takeyama, Akinori; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.377 - 379, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Chen, Z. Q.; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Xu, Y. H.; Sekiguchi, Takashi*
Applied Surface Science, 244(1-4), p.377 - 380, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:55.78(Chemistry, Physical)Homo- and heteroepitaxial ZnO films were grown by pulsed laser deposition on single crystal ZnO substrate and Al O
O substrate, respectively. The surface roughness probed by atomic force microscope (AFM) depends strongly on the substrate, which is much larger for the heteroepitaxial layer. Doppler broadening of positron annihilation measurements show existence of defects in both of the films, with a higher concentration in the homoepitaxial film. Raman scattering measurements reveal the E2 phonon vibration mode at 437 cm
substrate, respectively. The surface roughness probed by atomic force microscope (AFM) depends strongly on the substrate, which is much larger for the heteroepitaxial layer. Doppler broadening of positron annihilation measurements show existence of defects in both of the films, with a higher concentration in the homoepitaxial film. Raman scattering measurements reveal the E2 phonon vibration mode at 437 cm , which is characteristic of the wurtzite structure. These films show strong ultraviolet (UV) emission at 3.3 eV from the cathodoluminescence measurements, which indicates good optical properties.
, which is characteristic of the wurtzite structure. These films show strong ultraviolet (UV) emission at 3.3 eV from the cathodoluminescence measurements, which indicates good optical properties.
Kumada, Takayuki; Karavitis, M.*; Goldschleger, I. U.*; Apkarian, V. A.*
Hoshasen Kagaku, (79), p.30 - 35, 2005/03
We should know how the high energy deposited by irradiation dissipates in materials in order to understand radiation chemical processes. In this study, we carried out TR-CARS (Time-Resolved Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) study of molecular iodine in solid krypton to understand the mechanism of vibrational relaxation in solid phase. Decoherence of the vibrational state is due to energy dissipation below 10 K whereas pure dephasing plays an important role above. We also found that the dephasing is due to the scattering with local phonon mode with the energy of 40 K.
 (v = 1-19) in solid Kr
(v = 1-19) in solid KrKaravitis, M.*; Kumada, Takayuki; Goldschleger, I. U.*; Apkarian, V. A.*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 7(5), p.791 - 796, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:69.43(Chemistry, Physical)Energy dissipation and phase relaxation of the vibrational quantum states of iodine molecules in solid krypton have been studied in the temperature range between 7 and 45 K using a technique of time-resolved coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering (CARS) spectroscopy by a femto-second laser. The rate of energy dissipation was independent of tempeature, but proportional to the vibrational quantum number v. The pure dephasing rate exponentially increased with an increase in temperature and was proportional to v . The energy relaxation was found to take place by transfering the vibrational energy of iodine to four phonons in the krypton solid. The pure dephasing was induced by elastic scattering with phonon. It was suggested by a computer simulation that the phonon which induced the pure dephasing accompanied libration mode of iodine molecules.
. The energy relaxation was found to take place by transfering the vibrational energy of iodine to four phonons in the krypton solid. The pure dephasing was induced by elastic scattering with phonon. It was suggested by a computer simulation that the phonon which induced the pure dephasing accompanied libration mode of iodine molecules.
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Noboru; Suzuki, Yoji; Sukegawa, Kota*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Kishimoto, Maki; Nagashima, Keisuke
JAERI-Tech 2004-062, 32 Pages, 2004/11
We have designed new chirp-pulse amplification (CPA) laser system for 0.1 Hz repetition rate soft X-ray laser system. We adopted the optical parametric chirped pulse amplifier (OPCPA) for a pre-amplifier because of its pulse controllability. For a main-amplifier, we decided to use a zigzag-slab amplifier because of its thermal radiation ability. In order to avoid the inhomogeneous spatial profile of the amplified laser beam, the image of the incident laser light created by a serrated aperture is transferred by use of an image relay system. In this report, we will show the preliminary test of each amplifier using a prototype system and the details of the final system design.
 thin films on glass substrate grown by pulsed laser deposition
thin films on glass substrate grown by pulsed laser depositionChoi, Y.; Yamamoto, Shunya; Umebayashi, Tsutomu; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Solid State Ionics, 172(1-4), p.105 - 108, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:82.31(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 )
) and CaCO
and CaCO crystals
crystalsDeki, Kyoichi*; Matsuoka, Fumiaki*; Tei, Kazuyoku*; Arisawa, Takashi
Reza Kenkyu, 31(12), p.854 - 859, 2003/12
no abstracts in English
Daido, Hiroyuki
Reza Kenkyu, 31(11), p.696 - 697, 2003/11
no abstracts in English